Updating LinuxCNC to a new minor release (ie to a new version in the same stable series, for example from 2.9.1 to 2.9.2) is an automatic process if your PC is connected to the internet. You will see an update prompt after a minor release along with other software updates. If you don’t have an internet connection to your PC see Updating without Network.
1. Upgrade auf die neue Version
This section describes how to upgrade LinuxCNC from version 2.8.x to a 2.9.y version. It assumes that you have an existing 2.8 install that you want to update.
To upgrade LinuxCNC from a version older than 2.8, you have to first upgrade your old install to 2.8, then follow these instructions to upgrade to the new version.
Wenn Sie keine alte Version von LinuxCNC zu aktualisieren haben, dann sind Sie am besten aus machen eine frische Installation der neuen Version, wie im Abschnitt LinuxCNC erhalten beschrieben.
Darüber hinaus ist es unter Ubuntu Precise oder Debian Wheezy eine Überlegung wert, ein Backup des "linuxcnc"-Verzeichnisses auf einem Wechselmedium vorzunehmen und eine Neuinstallaion des neuesn Betriebsystems und der LinuxCNC version durchzuführen, da diese Versionen des OS 2017 bzw. 2018 ausliefen. Wenn Sie Ubuntu Lucid nutzen, dann werden Sie dies tun müssen, da Lucid nicht mehr von LinuxCNC unterstützt wird (es war EOL im Jahr 2013).
To upgrade major versions like 2.8 to 2.9 when you have a network connection at the machine you need to disable the old linuxcnc.org apt sources in the file /etc/apt/sources.list and add a new linuxcnc.org apt source for 2.9, then upgrade LinuxCNC.
Die Details hängen von der Plattform ab, auf der Sie arbeiten. Öffnen Sie ein terminal und geben Sie lsb_release -ic ein, um diese Informationen herauszufinden:
lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: BusterYou should be running on Debian Buster, Bullseye or Bookworm or Ubuntu 20.04 "Focal Fossa" or newer. LinuxCNC 2.9.y will not run on older distributions than these.
Sie müssen auch prüfen, welcher Echtzeit-Kernel verwendet wird:
uname -r
6.1.0-10-rt-amd64Wenn Sie (wie oben) -rt- im Kernel-Namen sehen, dann laufen Sie mit dem preempt-rt Kernel und sollten die "uspace" Version von LinuxCNC installieren. Sie sollten auch uspace für "sim"-Konfigurationen auf Nicht-Echtzeit-Kerneln installieren
If you see -rtai- in the kernel name then you are running RTAI realtime. See below for the LinuxCNC version to install. RTAI packages are available for Bookworm and Buster but not currently for Bullseye.
1.1. Apt Sources Konfiguration
-
Open the
Software Sourceswindow. The process for doing this differs slightly on the three supported platforms:-
Debian:
-
Click on
Applications Menu, thenSystem, thenSynaptic Package Manager. -
Klicken Sie in Synaptic auf das Menü
Einstellungenund dann aufRepositories, um das FensterSoftwarequellenzu öffnen.
-
-
Ubuntu Precise:
-
Klicken Sie auf das Symbol "Dash Home" oben links.
-
Geben Sie in das Feld "Suche" den Begriff "Software" ein und klicken Sie dann auf das Symbol "Ubuntu Software Center".
-
Klicken Sie im Ubuntu Software Center-Fenster auf das Menü "Bearbeiten" und dann auf "Softwarequellen…", um das Fenster "Softwarequellen" zu öffnen.
-
-
Ubuntu Lucid:
-
Klicken Sie auf das Menü "System", dann auf "Verwaltung" und dann auf "Synaptic Package Manager".
-
Klicken Sie in Synaptic auf das Menü
Einstellungenund dann aufRepositories, um das FensterSoftwarequellenzu öffnen.
-
-
-
Wählen Sie im Fenster "Software-Quellen" die Registerkarte "Andere Software".
-
Löschen oder deaktivieren Sie alle alten linuxcnc.org-Einträge (lassen Sie alle nicht-linuxcnc.org-Zeilen unverändert).
-
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Hinzufügen" und fügen Sie eine neue apt-Zeile hinzu. Die Zeile wird auf den verschiedenen Plattformen etwas anders aussehen:
| OS / Realtime Version | Repository |
|---|---|
Debian Buster - preempt |
|
Debian-Knacker - RTAI |
|
Debian Bullseye - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - RTAI |
|
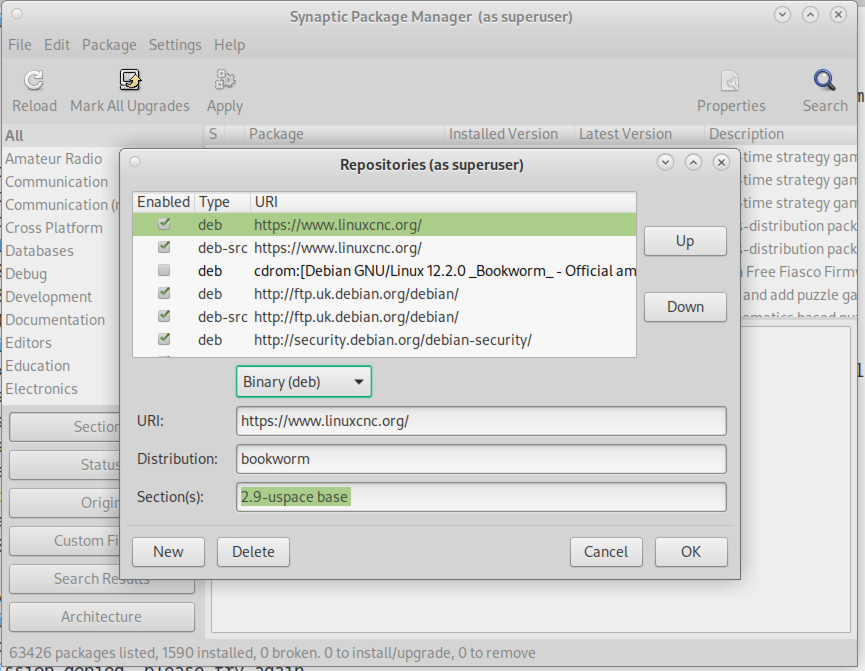
-
Klicken Sie im Fenster "Softwarequellen" auf "Quelle hinzufügen" und dann auf "Schließen". Wenn ein Fenster angezeigt wird, das Sie darüber informiert, dass die Informationen über die verfügbare Software veraltet sind, klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Neu laden".
1.2. Upgrade auf die neue Version
Da Ihr Computer nun weiß, wo er die neue Version der Software erhält, müssen wir sie nun installieren.
Der Prozess unterscheidet sich wiederum je nach Plattform.
1.2.1. Debian Buster, Bullseye and Bookworm
Debian uses the Synaptic Package Manager.
-
Öffnen Sie Synaptic gemäß den Anweisungen in Festlegen der apt sources oben.
-
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Neu laden".
-
Verwenden Sie die Suchfunktion, um nach
linuxcnczu suchen. -
Das Paket heißt „linuxcnc“ für RTAI-Kernel und „linuxcnc-uspace“ für preempt-rt.
-
Click the check box to mark the new linuxcnc and linuxcnc-doc-* packages for upgrade. The package manager may select a number of additional packages to be installed, to satisfy dependencies that the new linuxcnc package has.
-
Click the
Applybutton, and let your computer install the new package. The old linuxcnc package will be automatically upgraded to the new one.
1.3. Ubuntu
-
Klicken Sie auf das Symbol "Dash Home" oben links.
-
Geben Sie in das Feld "Suche" den Begriff "Update" ein und klicken Sie dann auf das Symbol "Update Manager".
-
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Prüfen", um die Liste der verfügbaren Pakete aufzurufen.
-
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Updates installieren", um die neuen Versionen aller Pakete zu installieren.
2. Aktualisieren ohne Netzwerk
To update without a network connection you need to download the .deb then install it with dpkg. The .debs can be found in https://linuxcnc.org/dists/ .
Sie müssen im obigen Link nach unten gehen, um das richtige Debian Paket (.deb Datei) für Ihre Installation zu finden. Öffnen Sie ein Terminal und geben Sie "lsb_release -ic" ein, um den Versions-Bezeichner Ihres Betriebssystems zu finden.
> lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: bullseyePick the OS from the list then pick the major version you want like 2.9-rt for RTAI or 2.9-rtpreempt or 2.9-uspace for preempt-rt.
Wählen Sie als Nächstes den Computertyp aus, den Sie haben: binary-amd64 für jeden 64-Bit-x86, binary-i386 für 32-Bit, binary-armhf (32-Bit) oder binary-arm64 (64-Bit) für Raspberry Pi.
Next pick the version you want from the bottom of the list like linuxcnc-uspace_2.8.0_amd64.deb (choose the latest by date). Download the deb and copy it to your home directory. You can rename the file to something a bit shorter with the file manager like linuxcnc_2.9.2.deb then open a terminal and install it with the package manager with this command:
sudo dpkg -i linuxcnc_2.9.2.deb3. Updating Configuration Files for 2.9
3.1. Stricter handling of pluggable interpreters
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t know what a pluggable interpreter is, then this section does not affect you.
A seldom-used feature of LinuxCNC is support for pluggable interpreters, controlled by the undocumented [TASK]INTERPRETER INI setting.
Versions of LinuxCNC before 2.9.0 used to handle an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER setting by automatically falling back to using the default G-code interpreter.
Since 2.9.0, an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER value will cause LinuxCNC to refuse to start up. Fix this condition by deleting the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting from your INI file, so that LinuxCNC will use the default G-code interpreter.
3.2. Canterp
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t use the canterp pluggable interpreter, then this section does not affect you.
In the extremely unlikely event that you are using canterp, know that the module has moved from /usr/lib/libcanterp.so to /usr/lib/linuxcnc/canterp.so, and the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting correspondingly needs to change from libcanterp.so to canterp.so.
4. Updating Configuration Files (for 2.9.y)
No changes should be necessary to configuration files when moving from 2.8.x to 2.9.y.
4.1. Spindle limits in the INI
It is now possible to add settings to the [SPINDLE] section of the INI file
MAX_FORWARD_VELOCITY = 20000 The maximum spindle speed (in rpm)
MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY = 3000 The minimum spindle speed (in rpm)
MAX_REVERSE_VELOCITY = 20000 This setting will default to MAX_FORWARD_VELOCITY if omitted.
MIN_REVERSE_VELOCITY = 3000` This setting is equivalent to MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY but for reverse spindle rotation. It will default to the MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY if omitted.
INCREMENT = 200 Sets the step size for spindle speed increment / decrement commands. This can have a different value for each spindle. This setting is effective with AXIS and Touchy but note that some control screens may handle things differently.
HOME_SEARCH_VELOCITY = 100 - Accepted but currently does nothing
HOME_SEQUENCE = 0 - Accepted but currently does nothing
5. New HAL components
5.1. Non-Realtime
mdro mqtt-publisher pi500_vfd pmx485-test qtplasmac-cfg2prefs qtplasmac-materials qtplasmac-plasmac2qt qtplasmac-setup sim-torch svd-ps_vfd
5.2. Echtzeit
anglejog div2 enum filter_kalman flipflop hal_parport homecomp limit_axis mesa_uart millturn scaled_s32_sums tof ton
6. New Drivers
A framework for controlling ModBus devices using the serial ports on many Mesa cards has been introduced. http://linuxcnc.org/docs/2.9/html/drivers/mesa_modbus.html
A new GPIO driver for any GPIO which is supported by the gpiod library is now included: http://linuxcnc.org/docs/2.9/html/drivers/hal_gpio.html