Updating LinuxCNC to a new minor release (ie to a new version in the same stable series, for example from 2.9.7 to 2.9.8) is an automatic process if your PC is connected to the internet. You will see an update prompt after a minor release along with other software updates. If you don’t have an internet connection to your PC see Updating without Network.
1. Oppgradering til den nye versjonen
Dette avsnittet beskriver hvordan oppgradere LinuxCNC fra versjon 2.8.x til en 2.9.y-versjon. Den antar at du har en eksisterende 2.8-installasjon som du ønsker å oppdatere.
For å oppgradere LinuxCNC fra en versjon eldre enn 2.8 så må du først oppgradere din gamle installasjon til 2.8 og så følge disse instruksjonene for å oppgradere til den nye versjonen.
Hvis du ikke har en gammel versjon av LinuxCNC å oppgradere så er det bedre tjent med å installere en ny versjon som beskrevet i avsnittet Skaffe LinuxCNC.
Furthermore, if you are running Ubuntu Precise, Debian Wheezy or Debian Buster it is well worth considering making a backup of the "linuxcnc" directory on removable media and performing a clean install of a newer OS and LinuxCNC version as these releases were EOL in 2017, 2018 and 2022 respectively. If you are running on Ubuntu Lucid then you will have to do this, as Lucid is no longer supported by LinuxCNC (it was EOL in 2013).
For å oppgradere hovedversjoner som 2.8 til 2.9 når du har en nettforbindelse på maskinen, så må du koble ut de gamle linuxcnc.org-apt-kildene i filen /etc/apt/sources.list og legge til en ny linuxcnc.org-apt-kilde for 2.9 for så å oppgradere LinuxCNC.
Detaljene avhenger av hvilken platform du kjører på. Åpne en terminal, skriv så `lsb_release -ic`for å finne informasjon om dette:
lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: TrixieYou should be running on Debian Bullseye, Bookworm or Trixie or Ubuntu 20.04 "Focal Fossa" or newer. LinuxCNC 2.9.y will not run on older distributions than these.
Du må også sjekke hvilken sanntidskjerne som brukes:
uname -r
6.1.0-10-rt-amd64Hvis du ser (som over) -rt i kjernenavnet så kjører du en «preemt-rt»-kjerne og bør installere «uspace»-utgaven av LinuxCNC. Du bør også installere denne for simulert oppsett på ikkesanntidskjerner.
If you see -rtai- in the kernel name then you are running RTAI realtime. See below for the LinuxCNC version to install. RTAI packages are available for Bookworm and Buster but not currently for Bullseye.
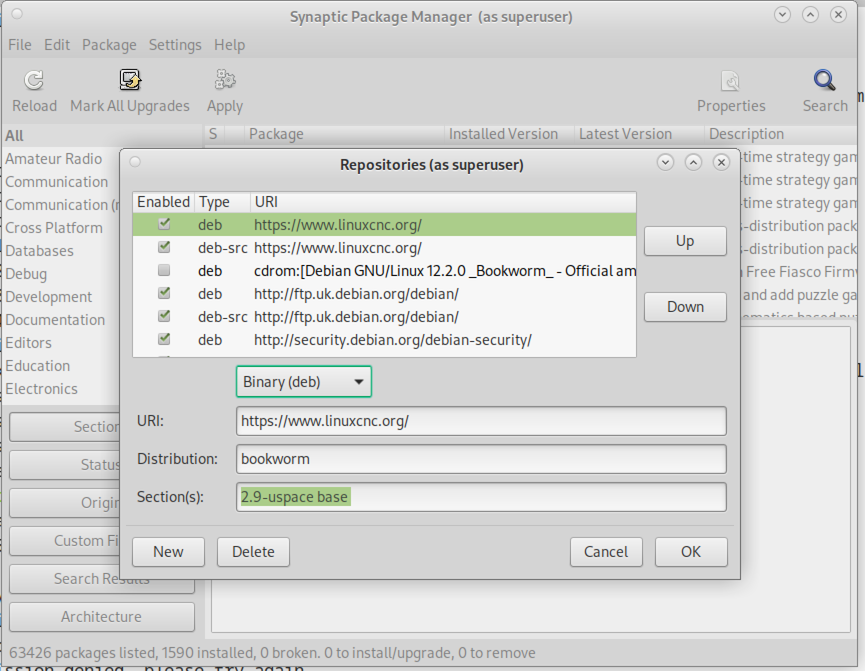
1.1. Apt-kildeoppsett
-
Åpne
Software Sources-vinduet. Prosessen for å gjøre dette varierer litt på de tre støttede platformene:-
Debian:
-
Klikk på
Applications Menu, deretterSystem, såSynaptic Package Manager. -
Klikk på
Oppsett-menyen i Synaptic, klikk så påRepositoriesfor å åpneSoftware Sources-vinduet.
-
-
Ubuntu Precise:
-
Click on the
Dash Homeicon in the top left. -
In the
Searchfield, type "software", then click on theUbuntu Software Centericon. -
In the Ubuntu Software Center window, click on the
Editmenu, then click onSoftware Sources...to open theSoftware Sourceswindow.
-
-
Ubuntu Lucid:
-
Click the
Systemmenu, thenAdministration, thenSynaptic Package Manager. -
In Synaptic, click on the
Settingsmenu, then click onRepositoriesto open theSoftware Sourceswindow.
-
-
-
In the
Software Sourceswindow, select theOther Softwaretab. -
Delete or un-check all the old linuxcnc.org entries (leave all non-linuxcnc.org lines as they are).
-
Click the
Addbutton and add a new apt line. The line will be slightly different on the different platforms:
| OS / Sanntidsversjon | Depot |
|---|---|
Debian Bullseye - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - RTAI |
|
Debian Trixie - preempt |
|
Debian Trixie - RTAI |
|
-
Click
Add Source, thenClosein the Software Sources window. If it pops up a window informing you that the information about available software is out-of-date, click theReloadbutton.
1.2. Upgrading to the new version
Now your computer knows where to get the new version of the software, next we need to install it.
Igjen så er prosessen annerledes avhengig av platformen din.
1.2.1. Debian Bullseye, Bookworm and Trixie
Debian uses the Synaptic Package Manager.
-
Open Synaptic using the instructions in Setting apt sources above.
-
Click the
Reloadbutton. -
Use the Search function to search for
linuxcnc. -
The package is called "linuxcnc" for RTAI kernels and "linuxcnc-uspace" for preempt-rt.
-
Click the check box to mark the new linuxcnc and linuxcnc-doc-* packages for upgrade. The package manager may select a number of additional packages to be installed, to satisfy dependencies that the new linuxcnc package has.
-
Click the
Applybutton, and let your computer install the new package. The old linuxcnc package will be automatically upgraded to the new one.
1.3. Ubuntu
-
Click on the
Dash Homeicon in the top left. -
In the
Searchfield, type "update", then click on theUpdate Managericon. -
Click the
Checkbutton to fetch the list of packages available. -
Click the
Install Updatesbutton to install the new versions of all packages.
2. Updating without Network
To update without a network connection you need to download the .deb then install it with dpkg. The .debs can be found in https://linuxcnc.org/dists/ .
You have to drill down from the above link to find the correct deb for your installation. Open a terminal and type in lsb_release -ic to find the release name of your OS.
> lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: trixiePick the OS from the list then pick the major version you want like 2.9-rt for RTAI or 2.9-uspace for preempt-rt.
Next pick the type of computer you have: binary-amd64 for 64-bit PC or binary-arm64 (64bit) for Raspberry Pi.
Next pick the version you want from the bottom of the list like linuxcnc-uspace_2.9.8_amd64.deb (choose the latest by date). Download the deb and copy it to your home directory. You can rename the file to something a bit shorter with the file manager like linuxcnc_2.9.8.deb then open a terminal and install it with the package manager with this command:
sudo dpkg -i linuxcnc_2.9.8.deb3. Oppdatering av oppsettfiler for 2.9
3.1. Stricter handling of pluggable interpreters
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t know what a pluggable interpreter is, then this section does not affect you.
A seldom-used feature of LinuxCNC is support for pluggable interpreters, controlled by the undocumented [TASK]INTERPRETER INI setting.
Versions of LinuxCNC before 2.9.0 used to handle an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER setting by automatically falling back to using the default G-code interpreter.
Since 2.9.0, an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER value will cause LinuxCNC to refuse to start up. Fix this condition by deleting the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting from your INI file, so that LinuxCNC will use the default G-code interpreter.
3.2. Canterp
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t use the canterp pluggable interpreter, then this section does not affect you.
In the extremely unlikely event that you are using canterp, know that the module has moved from /usr/lib/libcanterp.so to /usr/lib/linuxcnc/canterp.so, and the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting correspondingly needs to change from libcanterp.so to canterp.so.
3.3. Spindle limits in the INI
It is now possible to add settings to the [SPINDLE] section of the INI file
MAX_FORWARD_VELOCITY = 20000 The maximum spindle speed (in rpm)
MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY = 3000 The minimum spindle speed (in rpm)
MAX_REVERSE_VELOCITY = 20000 This setting will default to MAX_FORWARD_VELOCITY if omitted.
MIN_REVERSE_VELOCITY = 3000` This setting is equivalent to MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY but for reverse spindle rotation. It will default to the MIN_FORWARD_VELOCITY if omitted.
INCREMENT = 200 Sets the step size for spindle speed increment / decrement commands. This can have a different value for each spindle. This setting is effective with AXIS and Touchy but note that some control screens may handle things differently.
HOME_SEARCH_VELOCITY = 100 - Accepted but currently does nothing
HOME_SEQUENCE = 0 - Aksepteres men gjør for tiden ingen ting
4. Updating Configuration Files for 2.10.y
Touchy: the Touchy MACRO entries should now be placed in a [MACROS] section of the INI rather than in the [TOUCHY] section. This is part of a process of commonising the INI setting between GUIs.
5. New HAL components
5.1. Ikke-sanntid
mdro mqtt-publisher pi500_vfd pmx485-test qtplasmac-cfg2prefs qtplasmac-materials qtplasmac-plasmac2qt qtplasmac-setup sim-torch svd-ps_vfd
5.2. Sanntid
anglejog div2 enum filter_kalman flipflop homecomp limit_axis mesa_uart millturn scaled_s32_sums tof ton
6. Nye drivere
Et rammeverk for å kontrollere ModBus-enheter med serieporter på mange Mesakort har blitt introdusert. http://linuxcnc.org/docs/2.9/html/drivers/mesa_modbus.html
En ny GPIO-driver for enhver GPIO som støttes av gpiod-biblioteket er nå med: http://linuxcnc.org/docs/2.9/html/drivers/hal_gpio.html